Items filtered by date: September 2021
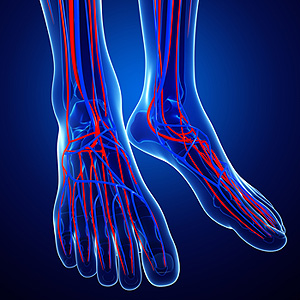
Causes Symptoms and Treatment for Poor Circulation in the Feet
The purpose of the body’s circulation system is to transport blood, oxygen, and nutrients throughout the body. A reduction of blood to a specific part of the body may cause one to experience symptoms of poor circulation. The most common causes of poor circulation in the feet are obesity, diabetes, and heart conditions such as peripheral artery disease (PAD). Common symptoms of poor circulation include tingling, numbness, throbbing, pain and muscle cramps.
Peripheral artery disease is a common cause of poor circulation in the legs. Symptoms of PAD are cramping, pain or tiredness in the leg or hip muscles while walking or climbing stairs. This pain tends to go away with rest and starts back up when you begin to walk. It is a condition that causes the blood vessels and arteries to become narrow. Although PAD is more common in adults over the age of 50, it may also occur in younger people. A similar condition called atherosclerosis causes arteries to stiffen up due to a buildup of plaque in the arteries and blood vessels.
Blood clots are also a common cause of poor circulation in the feet. Clots may obstruct blood vessels and if they occur in the legs, they may eventually lead to pain and discoloration. This occurrence is commonly known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and it may travel to the lungs. Varicose veins are another condition that may lead to poor circulation, and it is caused by incompetence of the valves in the veins. Women who are overweight are prone to developing this condition. Lastly, diabetes, which is correlated with poor blood sugar metabolism may lead to chronic poor circulation. Those with diabetes often suffer from cramping in the legs, calves, thighs and buttocks.
If you are looking for ways to avoid poor circulation there are some tips you can follow. One tip is to avoid sitting for too long. If you plan to sit down for a long period of time, you should try standing up occasionally, to improve your circulation. Another great way to avoid poor circulation is to exercise. Exercise is an excellent way to pump the heart and increase blood flow. Those who suffer from poor circulation should also avoid smoking, reduce their salt intake, and try to lose weight.
If you are experiencing symptoms from poor circulation in your feet, you should consult with your podiatrist to determine the best method for treatment for you. He or she may prescribe medication in addition to recommending specific lifestyle changes to improve your circulation.
Exercises That May Boost Circulation
Reduced blood flow in the lower limbs can be a common problem as you get older. If you have poor circulation in your feet and ankles, exercising regularly may help. There are a variety of exercises that are tailored to your specific needs and abilities that you can do. Taking regular walks is just one low-cost way to get moving. You can also exercise your legs with stretches while laying down, sitting, or standing. If you sit at a desk for work, you might incorporate some quick heel and toe raises. To do this exercise, sit with both feet flat on the floor in front of you. Raise both of your heels and hold for three seconds. Repeat this 10 times. Next, raise just your toes and hold for three seconds. Repeat 10 times. For more information on how to increase lower limb circulation, please consult with a podiatrist.
While poor circulation itself isn’t a condition; it is a symptom of another underlying health condition you may have. If you have any concerns with poor circulation in your feet contact Dr. John Branwell of Kearny, New Jersey. Our doctor will treat your foot and ankle needs.
Poor Circulation in the Feet
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) can potentially lead to poor circulation in the lower extremities. PAD is a condition that causes the blood vessels and arteries to narrow. In a linked condition called atherosclerosis, the arteries stiffen up due to a buildup of plaque in the arteries and blood vessels. These two conditions can cause a decrease in the amount of blood that flows to your extremities, therefore resulting in pain.
Symptoms
Some of the most common symptoms of poor circulation are:
- Numbness
- Tingling
- Throbbing or stinging pain in limbs
- Pain
- Muscle Cramps
Treatment for poor circulation often depends on the underlying condition that causes it. Methods for treatment may include insulin for diabetes, special exercise programs, surgery for varicose veins, or compression socks for swollen legs.
As always, see a podiatrist as he or she will assist in finding a regimen that suits you. A podiatrist can also prescribe you any needed medication.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact our office located in Kearny, NJ . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.
Causes Symptoms and Treatment for Poor Circulation in the Feet
The purpose of the body’s circulation system is to transport blood, oxygen, and nutrients throughout the body. A reduction of blood to a specific part of the body may cause one to experience symptoms of poor circulation. The most common causes of poor circulation in the feet are obesity, diabetes, and heart conditions such as peripheral artery disease (PAD). Common symptoms of poor circulation include tingling, numbness, throbbing, pain and muscle cramps.
Peripheral artery disease is a common cause of poor circulation in the legs. Symptoms of PAD are cramping, pain or tiredness in the leg or hip muscles while walking or climbing stairs. This pain tends to go away with rest and starts back up when you begin to walk. It is a condition that causes the blood vessels and arteries to become narrow. Although PAD is more common in adults over the age of 50, it may also occur in younger people. A similar condition called atherosclerosis causes arteries to stiffen up due to a buildup of plaque in the arteries and blood vessels.
Blood clots are also a common cause of poor circulation in the feet. Clots may obstruct blood vessels and if they occur in the legs, they may eventually lead to pain and discoloration. This occurrence is commonly known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and it may travel to the lungs. Varicose veins are another condition that may lead to poor circulation, and it is caused by incompetence of the valves in the veins. Women who are overweight are prone to developing this condition. Lastly, diabetes, which is correlated with poor blood sugar metabolism may lead to chronic poor circulation. Those with diabetes often suffer from cramping in the legs, calves, thighs and buttocks.
If you are looking for ways to avoid poor circulation there are some tips you can follow. One tip is to avoid sitting for too long. If you plan to sit down for a long period of time, you should try standing up occasionally, to improve your circulation. Another great way to avoid poor circulation is to exercise. Exercise is an excellent way to pump the heart and increase blood flow. Those who suffer from poor circulation should also avoid smoking, reduce their salt intake, and try to lose weight.
If you are experiencing symptoms from poor circulation in your feet, you should consult with your podiatrist to determine the best method for treatment for you. He or she may prescribe medication in addition to recommending specific lifestyle changes to improve your circulation.
Exercises That May Boost Circulation
Reduced blood flow in the lower limbs can be a common problem as you get older. If you have poor circulation in your feet and ankles, exercising regularly may help. There are a variety of exercises that are tailored to your specific needs and abilities that you can do. Taking regular walks is just one low-cost way to get moving. You can also exercise your legs with stretches while laying down, sitting, or standing. If you sit at a desk for work, you might incorporate some quick heel and toe raises. To do this exercise, sit with both feet flat on the floor in front of you. Raise both of your heels and hold for three seconds. Repeat this 10 times. Next, raise just your toes and hold for three seconds. Repeat 10 times. For more information on how to increase lower limb circulation, please consult with a podiatrist.
While poor circulation itself isn’t a condition; it is a symptom of another underlying health condition you may have. If you have any concerns with poor circulation in your feet contact Dr. John Branwell of Kearny, New Jersey. Our doctor will treat your foot and ankle needs.
Poor Circulation in the Feet
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) can potentially lead to poor circulation in the lower extremities. PAD is a condition that causes the blood vessels and arteries to narrow. In a linked condition called atherosclerosis, the arteries stiffen up due to a buildup of plaque in the arteries and blood vessels. These two conditions can cause a decrease in the amount of blood that flows to your extremities, therefore resulting in pain.
Symptoms
Some of the most common symptoms of poor circulation are:
- Numbness
- Tingling
- Throbbing or stinging pain in limbs
- Pain
- Muscle Cramps
Treatment for poor circulation often depends on the underlying condition that causes it. Methods for treatment may include insulin for diabetes, special exercise programs, surgery for varicose veins, or compression socks for swollen legs.
As always, see a podiatrist as he or she will assist in finding a regimen that suits you. A podiatrist can also prescribe you any needed medication.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact our office located in Kearny, NJ . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.
Read more about Causes Symptoms and Treatment for Poor Circulation in the FeetHeel Spurs
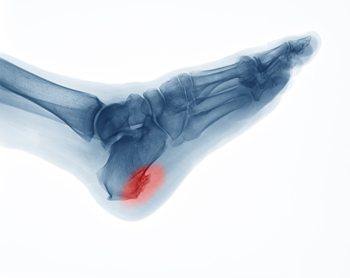
Heel spurs are the result of calcium deposits that cause bony protrusions on the underside of the heel. Heel spurs are usually painless, but they have the potential to cause heel pain. Heel spurs tend to be associated with plantar fasciitis, which is a condition that causes inflammation of the band of connective tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot. They most often occur to athletes whose sports involve a lot of running and jumping.
Some risk factors for developing heel spurs include running and jogging on hard surfaces, being obese, wearing poorly fitting shoes, or having walking gait abnormalities.
It is possible to have a heel spur without showing signs of any symptoms. However, if inflammation develops at the point of the spur’s formation, you may have pain while walking or running. In terms of diagnosis, sometimes all a doctor needs to know is that the patient is experiencing a sharp pain localized to the heel to diagnose a heel spur. Other times, an x-ray may be needed to confirm the presence of a heel spur.
Heel spurs can be prevented by wearing well-fitting shoes that have shock-absorbent soles. You should also be sure that you are choosing the right shoe for the activity you want to partake in; for example, do not wear walking shoes when you want to go on a run. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight can be beneficial toward preventing heel spurs, as it will prevent an excess amount of pressure being placed on the ligaments.
There are a variety of treatment options for people with heel spurs. Some of these include stretching exercises, physical therapy, shoe inserts, or taping and strapping to rest stressed muscles and tendons. If you have heel pain that lasts longer than a month, don’t hesitate to seek help from a podiatrist. Your doctor can help you determine which treatment option is best for you.
Where Do Heel Spurs Form?
Heel spurs are bony growths that can develop on the heels, usually due to small, repetitive traumas to the area. Heel spurs may develop from exercising, wearing poorly-fitted shoes, carrying excess body weight, or having an abnormal gait or arthritis. Heel spurs typically occur in one of two areas. Heel spurs that form on the back of the heel are associated with Achilles tendon inflammation. Heel spurs that form on the underside of the heel are associated with plantar fasciitis. In some cases heel spurs cause no symptoms and are only detected incidentally during X-rays. In other cases, heel spurs can cause pain, swelling, and tenderness. If you are experiencing any heel pain, please seek the care of a podiatrist.
Heel spurs can be incredibly painful and sometimes may make you unable to participate in physical activities. To get medical care for your heel spurs, contact Dr. John Branwell from Kearny, New Jersey. Our doctor will do everything possible to treat your condition.
Heels Spurs
Heel spurs are formed by calcium deposits on the back of the foot where the heel is. This can also be caused by small fragments of bone breaking off one section of the foot, attaching onto the back of the foot. Heel spurs can also be bone growth on the back of the foot and may grow in the direction of the arch of the foot.
Older individuals usually suffer from heel spurs and pain sometimes intensifies with age. One of the main condition's spurs are related to is plantar fasciitis.
Pain
The pain associated with spurs is often because of weight placed on the feet. When someone is walking, their entire weight is concentrated on the feet. Bone spurs then have the tendency to affect other bones and tissues around the foot. As the pain continues, the feet will become tender and sensitive over time.
Treatments
There are many ways to treat heel spurs. If one is suffering from heel spurs in conjunction with pain, there are several methods for healing. Medication, surgery, and herbal care are some options.
If you have any questions feel free to contact our office located in Kearny, NJ . We offer the latest in diagnostic and treatment technology to meet your needs.
Heel Spurs
Heel spurs are the result of calcium deposits that cause bony protrusions on the underside of the heel. Heel spurs are usually painless, but they have the potential to cause heel pain. Heel spurs tend to be associated with plantar fasciitis, which is a condition that causes inflammation of the band of connective tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot. They most often occur to athletes whose sports involve a lot of running and jumping.
Some risk factors for developing heel spurs include running and jogging on hard surfaces, being obese, wearing poorly fitting shoes, or having walking gait abnormalities.
It is possible to have a heel spur without showing signs of any symptoms. However, if inflammation develops at the point of the spur’s formation, you may have pain while walking or running. In terms of diagnosis, sometimes all a doctor needs to know is that the patient is experiencing a sharp pain localized to the heel to diagnose a heel spur. Other times, an x-ray may be needed to confirm the presence of a heel spur.
Heel spurs can be prevented by wearing well-fitting shoes that have shock-absorbent soles. You should also be sure that you are choosing the right shoe for the activity you want to partake in; for example, do not wear walking shoes when you want to go on a run. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight can be beneficial toward preventing heel spurs, as it will prevent an excess amount of pressure being placed on the ligaments.
There are a variety of treatment options for people with heel spurs. Some of these include stretching exercises, physical therapy, shoe inserts, or taping and strapping to rest stressed muscles and tendons. If you have heel pain that lasts longer than a month, don’t hesitate to seek help from a podiatrist. Your doctor can help you determine which treatment option is best for you.
Where Do Heel Spurs Form?
Heel spurs are bony growths that can develop on the heels, usually due to small, repetitive traumas to the area. Heel spurs may develop from exercising, wearing poorly-fitted shoes, carrying excess body weight, or having an abnormal gait or arthritis. Heel spurs typically occur in one of two areas. Heel spurs that form on the back of the heel are associated with Achilles tendon inflammation. Heel spurs that form on the underside of the heel are associated with plantar fasciitis. In some cases heel spurs cause no symptoms and are only detected incidentally during X-rays. In other cases, heel spurs can cause pain, swelling, and tenderness. If you are experiencing any heel pain, please seek the care of a podiatrist.
Heel spurs can be incredibly painful and sometimes may make you unable to participate in physical activities. To get medical care for your heel spurs, contact Dr. John Branwell from Kearny, New Jersey. Our doctor will do everything possible to treat your condition.
Heels Spurs
Heel spurs are formed by calcium deposits on the back of the foot where the heel is. This can also be caused by small fragments of bone breaking off one section of the foot, attaching onto the back of the foot. Heel spurs can also be bone growth on the back of the foot and may grow in the direction of the arch of the foot.
Older individuals usually suffer from heel spurs and pain sometimes intensifies with age. One of the main condition's spurs are related to is plantar fasciitis.
Pain
The pain associated with spurs is often because of weight placed on the feet. When someone is walking, their entire weight is concentrated on the feet. Bone spurs then have the tendency to affect other bones and tissues around the foot. As the pain continues, the feet will become tender and sensitive over time.
Treatments
There are many ways to treat heel spurs. If one is suffering from heel spurs in conjunction with pain, there are several methods for healing. Medication, surgery, and herbal care are some options.
If you have any questions feel free to contact our office located in Kearny, NJ . We offer the latest in diagnostic and treatment technology to meet your needs.
Read more about Heel Spurs